The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully conducted the second earth-bound maneuver (EBN#2) of its Aditya-L1 solar mission on Tuesday, September 5, 2023. The maneuver was carried out using the spacecraft’s onboard propulsion system and was aimed at raising its orbit to 282 km x 40225 km. The maneuver was performed successfully and the spacecraft is now in its desired orbit.
The Aditya-L1 mission is India’s first solar mission and is designed to study the Sun’s corona, the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere. The mission will use a suite of instruments to study the corona’s structure, dynamics, and evolution. The mission is expected to provide valuable insights into the Sun’s activity and its impact on Earth’s space weather.
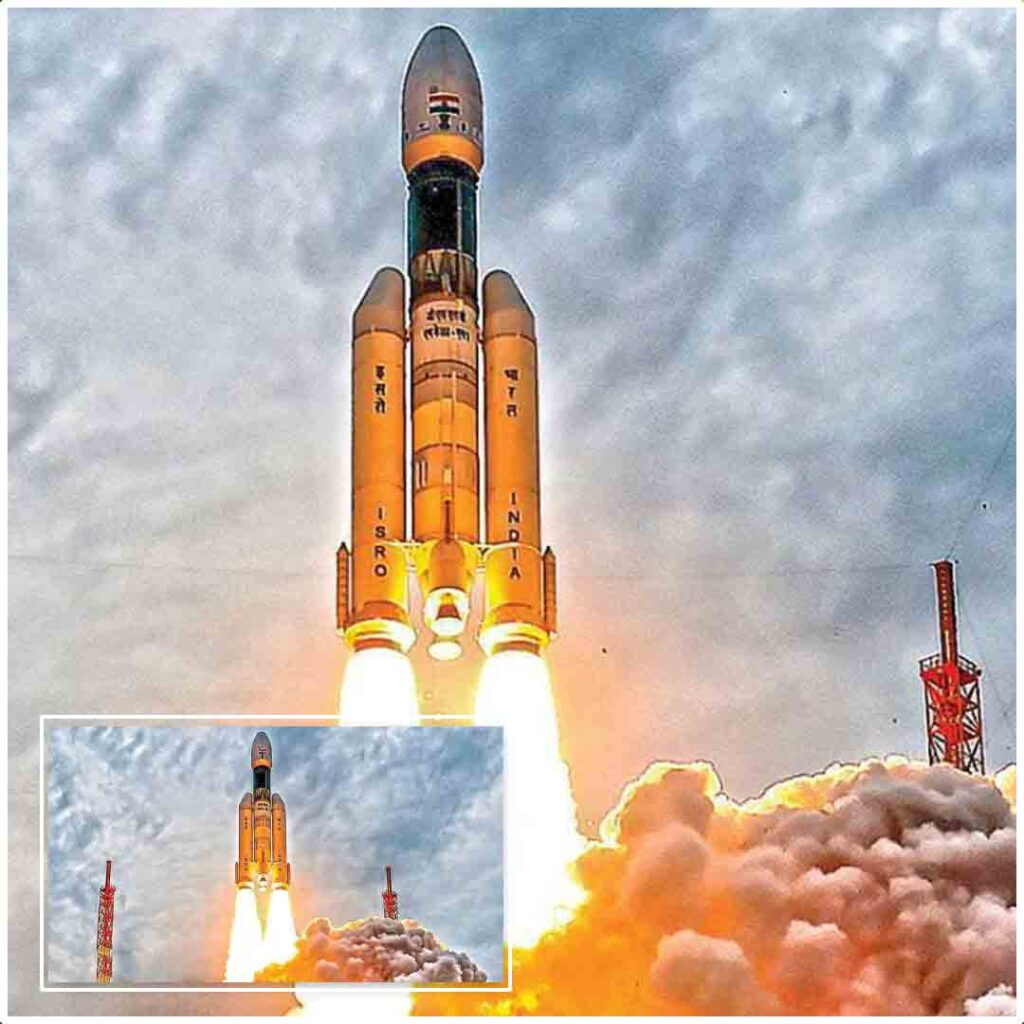

The second earth-bound maneuver was a critical milestone for the Aditya-L1 mission. It was the first time that the spacecraft’s propulsion system had been used since its launch on September 2, 2023. The successful completion of this maneuver is a major step towards the successful completion of the Aditya-L1 mission.
The next major maneuver for the Aditya-L1 mission is scheduled for September 10, 2023. This maneuver will be used to place the spacecraft in its final orbit around the Sun-Earth L1 point. The L1 point is a gravitationally stable location between the Sun and Earth, where the spacecraft will be able to continuously observe the Sun without any occultations.
The Aditya-L1 mission is expected to be operational for a period of five years. During this time, the spacecraft is expected to collect a wealth of data on the Sun’s corona. This data will be used to improve our understanding of the Sun’s activity and its impact on Earth’s space weather.
The successful completion of the second earth-bound maneuver is a major milestone for the Aditya-L1 mission. It is a testament to the hard work and dedication of the ISRO team. The mission is now well on its way to achieving its scientific objectives.
Here are some of the key features and objectives of the Aditya-L1 mission:
- The spacecraft will be placed in a halo orbit around the Sun-Earth L1 point, which is located roughly 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
- The spacecraft will carry a suite of instruments to study the Sun’s corona, including a coronagraph, a spectrograph, and a polarimeter.
- The mission is expected to provide valuable insights into the Sun’s activity and its impact on Earth’s space weather.
- The mission is expected to be operational for a period of five years.
The Aditya-L1 mission is a major milestone in India’s space program. It is the first Indian mission to study the Sun in detail and is expected to make significant contributions to our understanding of the Sun’s activity and its impact on Earth.






















